Linux命令 iptables
 iptables 详解及7层过滤
iptables 详解及7层过滤
2013-07-04 16:03:59
原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 、作者信息和本声明。否则将追究法律责任。http://freeloda.blog.51cto.com/2033581/1241545
大纲
一、防火墙简介
二、防火墙分类
三、防火墙在企业中的部署
四、IPTABLES的简介
五、IPTABLES的表和链
六、IPTABLES的几个状态
七、IPTABLES的命令及使用
八、IPTABLES的脚本编写
九、IPTABLES的7层过滤
注:本文的测试环境(CentOS 5.5 X86_64)
一、防火墙简介
防火墙其实就是一个加固主机或网络安全的一个设备或者软件而已,通过防火墙可以隔离风险区域与安全区域的连接,同时不会妨碍风险区域的访问。当然需要注意的是世界上没有绝对的安全,防火墙也只是启到一定的安全防护。大多数的安全风险还是在内网当中!
二、防火墙的分类
(1).从特点上分类
第一种,软件防火墙,软件防火墙需要运行在特定的计算机上,而且需要计算机的操作系统的支持。
第二种,硬件防火墙,硬件防火墙其实就是一个普通pc机的架构,然后上面跑有专门的操作系统。
第三种,芯片级的防火墙,这种防火墙基于专门的硬件平台,没有操作系统,专有的ASIC芯片使它们比其他类的防火墙速度更快,处理能力极强,性能更高,但是价格却极其昂贵。
(2).从技术上分类
第一种,包过滤型防火墙,这类的防火墙主要是工作在网络层,根据事先设定好的规则进行检查,检查结果根据事先设定好的处理机制进行处理。
第二种,应用层防火墙,它是工作在TCP/IP模型中的最高层应用层,相比较来说速度要慢一点。
第三种,状态监视器,状态监视做为防火墙其安全性为最佳,但配置比较复杂,且网络速度较慢。
三、防火墙在企业中的部署
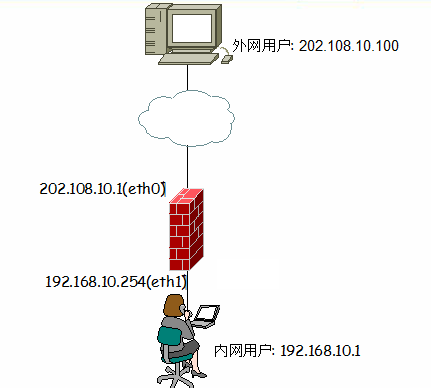
(1). 单宿主堡垒主机:是单台服务器有防火墙,只为单台服务器防护。
(2). 双宿主堡垒主机:双宿主堡垒主机是一台装有两块网卡的堡垒主机,一般这台堡垒主机应用在网关,防护局域网跟广域网之间通信等安全。
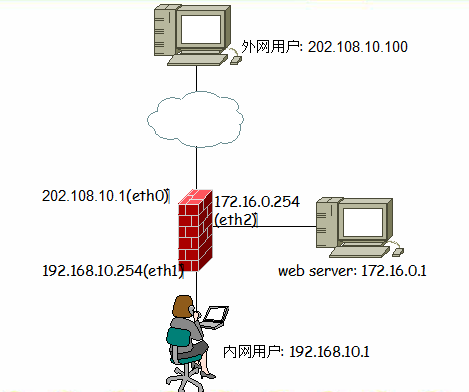
(3).三宿主堡垒主机:三宿主堡垒主机是一台装有三块网卡的堡垒主机,那么他将外网,内网,DMZ 三个区域隔离开来,同时保护内网已经DMZ区域的安全等。
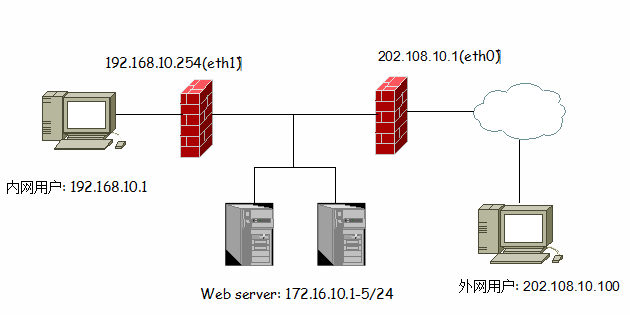
(4).背靠背型,如下图:
不用解释一看图就知道是怎么回事了,实际上前端防火墙是防护外网到DMZ区域以及到内网,后端防火墙是防护内网到DMZ区域的安全。好了说了这么多,下面我们说说iptables在linux中的应用!
四、IPTABLES的简介
IPTABLES/netfilter(官方网站,http://www.netfilter.org) 其实大多数人都认为iptables是linux系统上的一个服务,其实不是的. 我们linux系统上的服务比如说httpd服务在启动起来的时候,是不是在后台启动一个相应的服务进程且在网卡上监听一个端口,而iptables却不然,那么iptables到底是什么呢?其实iptables只是一个工具而已.我们的linux系统有用户空间,和内核空间,而iptables有两个组件,一是netfilter, netfilter组件只是用来过滤防火墙规则,及作出相应的处理机制的,它是集成在内核中的一部分,也就是说它是工作在内核空间的,那么大家都知道用户是不可能直接跟内核空间打交道的,那么netfilter只是工作在内核空间对规则进行处理的,那么规则从何而来呢? 是从iptables的第二个组件iptables而来的,我们上面说了IPTABLES只是一个工作在用户空间的一个工具而已,那么用户就使用这个工具的一个命令来跟工作在内核空间中的netfiter组件打交道的.其实IPTABLES防火墙就是这样的。
五、IPTABLES的表和链
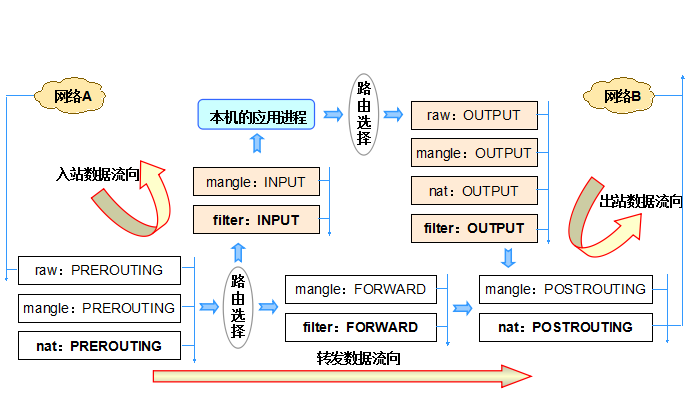
IPTABLES常用的表和链有三个,分别为 filter表 nat表 mangle表, 和五个链 INPUT链 OUTPUT链 FORWARE链 POSTROUTING链 PREROUTING链,下面来介绍下它们的各个功能,
1.filter表
filter表主要是过滤数据包的,IPTABLES几乎所有的数据包过滤都在此表中实现的,filter表也是IPTABLES中默认的表,此表中还包含三个链如下:
(1).INPUT链
过滤所有的目标地址是本机的数据包
(2).OUTPUT链
过滤所有从本机出去的数据包
(3).FORWORD链
过滤所有从本机路过的数据包
2.nat表
nat表主要是用于做网络地址转换的(NAT),在IPTABLES中可以做SNAT(源地址转换),DNAT(目标地址转换),PANT(即跟SNAT差不多,不一样的是SNAT的源地址是固定的,而PNAT的源地址是不固定的,当使用ppp或pppoe的方式连接互联网的时候一般适应这个) nat表中包含两个链如下:
(1).PREROUTING链
在数据包到达防火墙的时候改变目标地址 DNAT应用于此链.
(2).OUTPUT链
可以改变本地产生的数据包的目标地址
(3).POSTROUTING链
在数据包离开防火墙的时候改变源地址,SNAT应用于次链
3.mangle表
mangle表主要是修改数据包头部信息的,此表中包含以下5条链:
(1).PREROUTING链,
在数据包进入防火墙之后,也称为路由前,
(2).POSTROUTING链,
在数据包确定目标地址后,也称为路由后,
(3).OUTPUT链
从本机出去的时间包路由前
(4).INPUT链
数据包进入本机后,路由后
(5).FORWARD链
第一次路由判断之后,最后一次路由判断之前改变数据包
4.数据包过滤匹配流程
六、IPTABLES的几个状态
IPTABLES的状态跟踪连接有4种,分别是,NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED,INVALID,除了从本机出去的数据包有NAT表的OUTPUT链处理外,其他所有的状态跟踪都在NAT表中的PREROUTING链中处理,下面来说下4种状态是什么,
1.NEW状态
NEW状态的数据包说明这个数据包是收到的第一个数据包。
2.ESTABLISHED状态
只要发送并接到应答,一个数据包的状态就从NEW变为ESTABLEISHED,而且该状态会继续匹配这个连接后继数据包。
3.RELATED状态
当一个数据包的状态处于ESTABLSHED状态的连接有关系的时候,就会被认为是RELATED,也就是说一个链接想要是RELATED状态,首先要有一个ESTABLISHED的连接。
4.INVALID状态
不能被识别属于哪个连接状态或没有任何关系的状态,一般这中数据包要被拒绝的。
七、IPTABLES的命令及使用
iptables在CentOS或RHEL的系统上默认安装的, IPTABLES的命令选项主要分为这么几大类,规则管理,链管理,默认规则管理,查看,匹配条件,处理动作等,下面我们就来说明一下,
1.规则管理
> iptables -A 添加一条新规则 > iptables -I 插入一条新规则 -I 后面加一数字表示插入到哪行 > iptables -D 删除一条新规则 -D 后面加一数字表示删除哪行 > iptables -R 替换一条新规则 -R 后面加一数字表示替换哪行 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">2.链管理</span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > iptables -F 清空链中的所有规则 > iptables -N 新建一个链 > iptables -X 删除一个自定义链,删除之前要保证次链是空的,而且没有被引用 > iptables -E 重命名链 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">3.默认规则管理</span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > iptables -P 设置默认规则 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">4.查看</span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > iptables -L 查看规则 –L 还有几个子选项如下 > iptables -L -n 以数字的方式显示 > iptables -L -v 显示详细信息 > iptables -L -x 显示精确信息 > iptables -L --line-numbers 显示行号 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">5.条件匹配</span> > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">(1).基本匹配</span> > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">条件匹配也可以使用 ! 取反 </span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > -s 源地址 > -d 目标地址 > -p 协议{tcp|udp|icmp} > -i 从哪个网络接口进入,比如 -i eth0 > -o 从哪个网络接口出去,比如 -o eth0 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">(2).扩展匹配</span> > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">隐含扩展匹配</span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > -p {tcp|udp} --sport 指定源端口 > -p {tcp|udp} --dport 指定目标端口 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">显示扩展匹配</span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > -m state --state 匹配状态的 > -m mutiport --source-port 端口匹配 ,指定一组端口 > -m limit --limit 3/minute 每三分种一次 > -m limit --limit-burst 5 只匹配5个数据包 > -m string --string --algo bm|kmp --string "xxxx" 匹配字符串 > -m time --timestart 8:00 --timestop 12:00 表示从哪个时间到哪个时间段 > -m time --days 表示那天 > -m mac --mac-source xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx 匹配源MAC地址 > -m layer7 --l7proto qq 表示匹配腾讯qq的 当然也支持很多协议,这个默认是没有的,需要我们给内核打补丁并重新编译内核及iptables才可以使用 -m layer7 这个显示扩展匹配 > ``` > > <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">6.处理动作</span> > > ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; > -j ACCEPT 允许 > -j REJECT 拒绝 > -j DROP 拒绝并提示信息 > -j SNAT 源地址转换 > -j DNAT 目标地址转换 > -j REDIRECT 重定向 > -j MASQUERAED 地址伪装 > -j LOG --log-prefix "说明信息,自己随便定义" 记录日志 > ``` <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">八、IPTABLES的脚本编写</span> <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">IPTABLES 脚本里面其实就是敲的一系列命令而已下面给个例子,介绍下iptables命令的使用及IPTABLES脚本的编写 </span> <span style="font-size:14px;color:#000000;font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">1.IPTABLES脚本实例 </span> ``` brush:bash;toolbar:false; #vim iptables.sh #!/bin/bash # #定义变量 mynet=192.168.10.0/24 myip=192.168.10.100 IPT=/sbin/iptables #加载ftp模块 modprobe ip_conntrack-ftp modprobe ip_nat_ftp #开启路由转发功能 echo "1" /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward #清空所有表中的规则 $IPT -F $IPT -t nat –F $IPT -t mangle –F #删除所有自定义链 $IPT -X $IPT -t nat -X $IPT -t mangle –X #设置默认策略 $IPT -P INPUT DROP $IPT -P OUTPUT DROP $IPT -P FORWARD ACCEPT #允许状态为ESTABLISHED,RELATED的访问本机,及状态为NEW的从本机出去 $IPT -A INOUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT #允许本地环回口访问 $IPT -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT $IPT -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT #允许管理员主机访问本地ssh服务 $IPT -A INPUT -s $myip -m state --state NEW -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT $IPT -A OUTPUT -d $myip -p tcp --sport 22 -j ACCEPT #允许局域网的ping请求 $IPT -A INPUT -s $mynet -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT $IPT -A OUTPUT -d $mynet -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT #为局域网做SNAT $IPT -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s $mynet -j SNAT --to-source 222.95.1.97 #为局域网内部的web服务器做DNAT $IPT -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 222.95.1.97 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.10.1
2.让下次开机自动加载脚本
[root@localhost ~]# echo "/bin/bash /root/shell/iptables.sh" >> /etc/rc.local
九、IPTABLES的7层过滤
说明:为网络管理员,对P2P,QQ,酷狗,等软件是又爱又恨,大多数公司,为了提高工作效率禁止公司员工上QQ,看视频等, 在市场上买专门的上网行为管理设备,随便都是好几W,而使用linux来做网关,一样可以禁止qq,酷狗等软件,成本才几千块,下面将介绍下怎么实现的!
1.简介
在Linux的防火墙体系Netfilter下有一个独立的模块L7 filter 。从字面上看Netfilter是对网络数据的过滤,L7 filter是基于数据流应用层内容的过滤。不过实际上 L7 filter的本职工作不是对数据流进行过滤而是对数据流进行分类。它使用模式匹配算法把进入设备的数据包应用层内容与事先定义好的协议规则进行比对,如果匹配成功就说明这个数据包属于某种协议。
L7 filter是基于数据流工作的,建立在Netfilter connstrack功能之上。因为一个数据流或者说一个连接的所有数据都是属于同一个应用的,所以L7 filter没有必要对所以的数据包进行模式匹配,而只匹配一个流的前面几个数据包 (比如5或10个数据包)。当一个流的前面几个数据包包含了某种应用层协议的特征码时 (比如QQ),则这个数据流被L7 filter识别;当前面几个数据包的内容没有包含某种应用层协议的特征码时,则L7 filter放弃继续做模式匹配,这个数据流也就没有办法被识别。
2.下载相关软件
7层过滤首先需要内核支持,现在最新的内核是3.10(https://www.kernel.org/)但是L7 filter的支持列表只更新到2.6.30.5而且有部份的功能未经测试,而所有经过测试的版本的内核是2.6.28(http://l7-filter.sourceforge.net/kernelcompat),为了保证其稳定所以决定将内核升级为2.6.28!
[root@localhost src]# wget http://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v2.6/linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2
[root@localhost src]# wget http://netfilter.org/projects/iptables/files/iptables-1.4.7.tar.bz2
[root@localhost src]# wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/l7-filter/Protocol%20definitions/2009-05-28/l7-protocols-2009-05-28.tar.gz?use_mirror=nchc
[root@localhost src]# wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/l7-filter/l7-filter%20kernel%20version/2.22/netfilter-layer7-v2.22.tar.gz?use_mirror=nchc
[root@localhost src]# ll
total 52264
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 462420 Jan 3 2012 iptables-1.4.7.tar.bz2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 142050 May 29 2009 l7-protocols-2009-05-28.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 52665364 Dec 25 2008 linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 174853 Jul 14 2009 netfilter-layer7-v2.22.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]#
3.卸载系统自带的 iptables
在卸载之前,我们先把iptables的启动脚本及脚本配置文件拷贝到/root目录下待会有用
[root@localhost src]# cp /etc/init.d/iptables /root
[root@localhost src]# cp /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config /root
[root@localhost src]# rpm -qa | grep iptables
iptables-1.3.5-5.3.el5_4.1
iptables-ipv6-1.3.5-5.3.el5_4.1
[root@localhost src]# rpm -e --nodeps `rpm -qa | grep iptables`
warning: /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config saved as /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config.rpmsave
[root@localhost src]#
4.给新内核加入Layer 7补丁
[root@localhost src]# tar xf linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2 -C /usr/src
[root@localhost src]# tar xf netfilter-layer7-v2.22.tar.gz -C /usr/src
[root@localhost src]# cd /usr/src/
[root@localhost src]# ls
debug kernels linux-2.6.28 netfilter-layer7-v2.22 redhat
[root@localhost src]# ln -sv linux-2.6.28/ linux
create symbolic link `linux' to `linux-2.6.28/'
[root@localhost src]# ls
debug kernels linux linux-2.6.28 netfilter-layer7-v2.22 redhat
[root@localhost src]# cd /usr/src/linux
[root@localhost linux]# patch -p1 < ../netfilter-layer7-v2.22/kernel-2.
kernel-2.4-layer7-2.22.patch kernel-2.6.25-2.6.28-layer7-2.22.patch
[root@localhost linux]# patch -p1 < ../netfilter-layer7-v2.22/kernel-2.6.25-2.6.28-layer7-2.22.patch
patching file net/netfilter/Kconfig
patching file net/netfilter/Makefile
patching file net/netfilter/xt_layer7.c
patching file net/netfilter/regexp/regexp.c
patching file net/netfilter/regexp/regexp.h
patching file net/netfilter/regexp/regmagic.h
patching file net/netfilter/regexp/regsub.c
patching file net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_core.c
patching file net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_standalone.c
patching file include/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack.h
patching file include/linux/netfilter/xt_layer7.h
[root@localhost linux]# cp /boot/config-2.6.18-194.el5 /usr/src/linux/.config
5.编译内核
说明:(需要增加的编译模块)
Networking support → Networking Options → Network packet filtering framework → Core Netfilter Configuration
<M> Netfilter connection tracking support
<M> "layer7" match support
<M> "string" match support
<M> "time" match support
<M> "iprange" match support
<M> "connlimit" match support
<M> "state" match support
<M> "conntrack" connection match support
<M> "mac" address match support
<M> "multiport" Multiple port match support
Networking support → Networking Options →Network packet filtering framework → IP Netfilter Configuration
<M> IPv4 connection tracking support (required for NAT)
<M> Full NA
<M> MASQUERADE target support
<M> NETMAP target support
<M> REDIRECT target support
具体操作:
[root@localhost linux]#make menuconfig
HOSTCC scripts/basic/fixdep
HOSTCC scripts/basic/docproc
HOSTCC scripts/basic/hash
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/conf.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/kxgettext.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/checklist.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/inputbox.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/menubox.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/textbox.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/util.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/yesno.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/mconf.o
SHIPPED scripts/kconfig/zconf.tab.c
SHIPPED scripts/kconfig/lex.zconf.c
SHIPPED scripts/kconfig/zconf.hash.c
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/zconf.tab.o
HOSTLD scripts/kconfig/mconf
scripts/kconfig/mconf arch/x86/Kconfig
.config:1359:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for FIXED_PHY
.config:1659:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for ISDN
.config:2765:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for RTC_INTF_SYSFS
.config:2766:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for RTC_INTF_PROC
.config:2767:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for RTC_INTF_DEV
.config:2789:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for DMA_ENGINE
.config - Linux Kernel v2.6.28 Configuration
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌─────────────────────────────────────────── Linux Kernel Configuration ────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Arrow keys navigate the menu. <Enter> selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing <Y> │
│ includes, <N> excludes, <M> modularizes features. Press <Esc><Esc> to exit, <?> for Help, </> for Search. │
│ Legend: [*] built-in [ ] excluded <M> module < > module capable │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ General setup ---> │ │
│ │ [*] Enable loadable module support ---> │ │
│ │ -*- Enable the block layer ---> │ │
│ │ Processor type and features ---> │ │
│ │ Power management and ACPI options ---> │ │
│ │ Bus options (PCI etc.) ---> │ │
│ │ Executable file formats / Emulations ---> │ │
│ │ -*- Networking support ---> │ │
│ │ Device Drivers ---> │ │
│ │ Firmware Drivers ---> │ │
│ │ File systems ---> │ │
│ │ Kernel hacking ---> │ │
│ │ Security options ---> │ │
│ │ -*- Cryptographic API ---> │ │
│ │ [*] Virtualization (NEW) ---> │ │
│ │ Library routines ---> │ │
│ │ --- │ │
│ │ Load an Alternate Configuration File │ │
│ │ Save an Alternate Configuration File │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ <Select> < Exit > < Help > │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
.config - Linux Kernel v2.6.28 Configuration
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌─────────────────────────────────────────── Linux Kernel Configuration ────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Arrow keys navigate the menu. <Enter> selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing <Y> │
│ includes, <N> excludes, <M> modularizes features. Press <Esc><Esc> to exit, <?> for Help, </> for Search. │
│ Legend: [*] built-in [ ] excluded <M> module < > module capable │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ General setup ---> │ │
│ │ [*] Enable loadable module support ---> │ │
│ │ -*- Enable the block layer ---> │ │
│ │ Processor type and features ---> │ │
│ │ Power management and ACPI options ---> │ │
│ │ Bus options (PCI etc.) ---> │ │
│ │ Executable file formats / Emulations ---> │ │
│ │ -*- Networking support ---> │ │
│ │ Device Drivers ---> │ │
│ │ Firmware Drivers ---> │ │
│ │ File systems ---> │ │
│ │ Kernel hacking ---> │ │
│ │ Security options ---> │ │
│ │ -*- Cryptographic API ---> │ │
│ │ [*] Virtualization (NEW) ---> │ │
│ │ Library routines ---> │ │
│ │ --- │ │
│ │ Load an Alternate Configuration File │ │
│ │ Save an Alternate Configuration File │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ <Select> < Exit > < Help > │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
.config - Linux Kernel v2.6.28 Configuration
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────── Networking support ────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Arrow keys navigate the menu. <Enter> selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing <Y> │
│ includes, <N> excludes, <M> modularizes features. Press <Esc><Esc> to exit, <?> for Help, </> for Search. │
│ Legend: [*] built-in [ ] excluded <M> module < > module capable │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ --- Networking support │ │
│ │ Networking options ---> │ │
│ │ [ ] Amateur Radio support ---> │ │
│ │ < > CAN bus subsystem support (NEW) ---> │ │
│ │ < > IrDA (infrared) subsystem support ---> │ │
│ │ <M> Bluetooth subsystem support ---> │ │
│ │ < > RxRPC session sockets (NEW) │ │
│ │ < > Phonet protocols family (NEW) │ │
│ │ [*] Wireless (NEW) ---> │ │
│ │ {M} RF switch subsystem support ---> │ │
│ │ < > Plan 9 Resource Sharing Support (9P2000) (Experimental) (NEW) ---> │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ <Select> < Exit > < Help > │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
.config - Linux Kernel v2.6.28 Configuration
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────── Networking options ────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Arrow keys navigate the menu. <Enter> selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing <Y> │
│ includes, <N> excludes, <M> modularizes features. Press <Esc><Esc> to exit, <?> for Help, </> for Search. │
│ Legend: [*] built-in [ ] excluded <M> module < > module capable │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────↑(-)───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ <M> IP: ESP transformation │ │
│ │ <M> IP: IPComp transformation │ │
│ │ <M> IP: IPsec transport mode │ │
│ │ <M> IP: IPsec tunnel mode │ │
│ │ <*> IP: IPsec BEET mode (NEW) │ │
│ │ {*} Large Receive Offload (ipv4/tcp) │ │
│ │ <M> INET: socket monitoring interface │ │
│ │ [*] TCP: advanced congestion control ---> │ │
│ │ [ ] TCP: MD5 Signature Option support (RFC2385) (EXPERIMENTAL) (NEW) │ │
│ │ <M> The IPv6 protocol ---> │ │
│ │ [*] NetLabel subsystem support │ │
│ │ -*- Security Marking │ │
│ │ [*] Network packet filtering framework (Netfilter) ---> │ │
│ │ <M> The DCCP Protocol (EXPERIMENTAL) ---> │ │
│ │ -M- The SCTP Protocol (EXPERIMENTAL) ---> │ │
│ │ <M> The TIPC Protocol (EXPERIMENTAL) ---> │ │
│ │ <M> Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) │ │
│ │ <M> Classical IP over ATM │ │
│ │ [ ] Do NOT send ICMP if no neighbour │ │
│ └────────────────────↓(+)───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ <Select> < Exit > < Help > │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
.config - Linux Kernel v2.6.28 Configuration
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌───────────────────────────────── Network packet filtering framework (Netfilter) ──────────────────────────────────┐
│ Arrow keys navigate the menu. <Enter> selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing <Y> │
│ includes, <N> excludes, <M> modularizes features. Press <Esc><Esc> to exit, <?> for Help, </> for Search. │
│ Legend: [*] built-in [ ] excluded <M> module < > module capable │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ --- Network packet filtering framework (Netfilter) │ │
│ │ [ ] Network packet filtering debugging │ │
│ │ [*] Advanced netfilter configuration (NEW) │ │
│ │ [*] Bridged IP/ARP packets filtering │ │
│ │ Core Netfilter Configuration ---> │ │
│ │ <M> IP virtual server support ---> │ │
│ │ IP: Netfilter Configuration ---> │ │
│ │ IPv6: Netfilter Configuration ---> │ │
│ │ <M> Ethernet Bridge tables (ebtables) support ---> │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ <Select> < Exit > < Help > │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
.config - Linux Kernel v2.6.28 Configuration
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌────────────────────────────────────────── Core Netfilter Configuration ───────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Arrow keys navigate the menu. <Enter> selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing <Y> │
│ includes, <N> excludes, <M> modularizes features. Press <Esc><Esc> to exit, <?> for Help, </> for Search. │
│ Legend: [*] built-in [ ] excluded <M> module < > module capable │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────↑(-)───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ <M> "multiport" Multiple port match support │ │
│ │ <M> "owner" match support │ │
│ │ <M> IPsec "policy" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "physdev" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "pkttype" packet type match support │ │
│ │ <M> "quota" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "rateest" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "realm" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "recent" match support │ │
│ │ [*] Enable obsolete /proc/net/ipt_recent │ │
│ │ <M> "sctp" protocol match support (EXPERIMENTAL) │ │
│ │ <M> "state" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "layer7" match support │ │
│ │ [*] Layer 7 debugging output │ │
│ │ <M> "statistic" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "string" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "tcpmss" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "time" match support │ │
│ │ <M> "u32" match support │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ <Select> < Exit > < Help > │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Do you wish to save your new kernel configuration? │
│ <ESC><ESC> to continue. │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ < Yes > < No > │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
#
# configuration written to .config
#
*** End of Linux kernel configuration.
*** Execute 'make' to build the kernel or try 'make help'.
[root@localhost linux]# make
[root@localhost linux]# make modules_install
[root@localhost linux]# make install
[root@localhost linux]# vim /boot/grub/grub.conf #更改启动项
# grub.conf generated by anaconda
#
# Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file
# NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that
# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg.
# root (hd0,0)
# kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/sda2
# initrd /initrd-version.img
#boot=/dev/sda
default=1 #修改为0
timeout=5
splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz
hiddenmenu
title CentOS (2.6.28l7)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.28l7 ro root=LABEL=/
initrd /initrd-2.6.28l7.img
title CentOS (2.6.18-194.el5)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-194.el5 ro root=LABEL=/
initrd /initrd-2.6.18-194.el5.img
[root@localhost linux]# reboot #重新启动
[root@localhost ~]# uname -r #查看编译好的内核
2.6.28l7
6.编译安装iptables并支持Layer 7
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf iptables-1.4.7.tar.bz2 -C /usr/src
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/src/linux
[root@localhost linux]# cp /usr/src/netfilter-layer7-v2.22/iptables-1.4.3forward-for-kernel-2.6.20forward/* extensions/
[root@localhost linux]#./configure --prefix=/usr --with-ksource=/usr/src/linux
[root@localhost linux]# make && make install
[root@localhost linux]# iptables –V
[root@localhost ~]# cp iptables-config /etc/sysconfig/ #复制配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# cp iptables /etc/init.d/ #复制sysV脚本
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/iptables
[root@localhost ~]# which iptables
/usr/sbin/iptables
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/init.d/iptables #把所有/sbin/$IPTABLES替换为/usr/sbin/$IPTABLES 在vim命令模式下:%s@/sbin/$IPTABLES@/usr/sbin/$IPTABLES@g 然后保存退出
修改后的配置
#!/bin/sh
#
# iptables Start iptables firewall
#
# chkconfig: 2345 08 92
# description: Starts, stops and saves iptables firewall
#
# config: /etc/sysconfig/iptables
# config: /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config
# Source function library.
. /etc/init.d/functions
IPTABLES=iptables
IPTABLES_DATA=/etc/sysconfig/$IPTABLES
IPTABLES_CONFIG=/etc/sysconfig/${IPTABLES}-config
IPV=${IPTABLES%tables} # ip for ipv4 | ip6 for ipv6
PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES=/proc/net/${IPV}_tables_names
VAR_SUBSYS_IPTABLES=/var/lock/subsys/$IPTABLES
if [ ! -x /usr/sbin/$IPTABLES ]; then
echo -n $"/usr/sbin/$IPTABLES does not exist."; warning; echo
exit 0
fi
if lsmod 2>/dev/null | grep -q ipchains ; then
echo -n $"ipchains and $IPTABLES can not be used together."; warning; echo
exit 1
fi
# Old or new modutils
/sbin/modprobe --version 2>&1 | grep -q module-init-tools \
&& NEW_MODUTILS=1 \
|| NEW_MODUTILS=0
# Default firewall configuration:
IPTABLES_MODULES=""
IPTABLES_MODULES_UNLOAD="yes"
IPTABLES_SAVE_ON_STOP="no"
IPTABLES_SAVE_ON_RESTART="no"
IPTABLES_SAVE_COUNTER="no"
IPTABLES_STATUS_NUMERIC="yes"
IPTABLES_SYSCTL_LOAD_LIST=""
# Load firewall configuration.
[ -f "$IPTABLES_CONFIG" ] && . "$IPTABLES_CONFIG"
rmmod_r() {
# Unload module with all referring modules.
# At first all referring modules will be unloaded, then the module itself.
local mod=$1
local ret=0
local ref=
# Get referring modules.
# New modutils have another output format.
[ $NEW_MODUTILS = 1 ] \
&& ref=`lsmod | awk "/^${mod}/ { print \\\$4; }" | tr ',' ' '` \
|| ref=`lsmod | grep ^${mod} | cut -d "[" -s -f 2 | cut -d "]" -s -f 1`
# recursive call for all referring modules
for i in $ref; do
rmmod_r $i
let ret+=$?;
done
# Unload module.
# The extra test is for 2.6: The module might have autocleaned,
# after all referring modules are unloaded.
if grep -q "^${mod}" /proc/modules ; then
modprobe -r $mod > /dev/null 2>&1
let ret+=$?;
fi
return $ret
}
flush_n_delete() {
# Flush firewall rules and delete chains.
[ -e "$PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES" ] || return 1
# Check if firewall is configured (has tables)
tables=`cat $PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES 2>/dev/null`
[ -z "$tables" ] && return 1
echo -n $"Flushing firewall rules: "
ret=0
# For all tables
for i in $tables; do
# Flush firewall rules.
$IPTABLES -t $i -F;
let ret+=$?;
# Delete firewall chains.
$IPTABLES -t $i -X;
let ret+=$?;
# Set counter to zero.
$IPTABLES -t $i -Z;
let ret+=$?;
done
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && success || failure
echo
return $ret
}
set_policy() {
# Set policy for configured tables.
policy=$1
# Check if iptable module is loaded
[ ! -e "$PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES" ] && return 1
# Check if firewall is configured (has tables)
tables=`cat $PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES 2>/dev/null`
[ -z "$tables" ] && return 1
echo -n $"Setting chains to policy $policy: "
ret=0
for i in $tables; do
echo -n "$i "
case "$i" in
raw)
$IPTABLES -t raw -P PREROUTING $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t raw -P OUTPUT $policy \
|| let ret+=1
;;
filter)
$IPTABLES -t filter -P INPUT $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t filter -P OUTPUT $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t filter -P FORWARD $policy \
|| let ret+=1
;;
nat)
$IPTABLES -t nat -P PREROUTING $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t nat -P POSTROUTING $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t nat -P OUTPUT $policy \
|| let ret+=1
;;
mangle)
$IPTABLES -t mangle -P PREROUTING $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t mangle -P POSTROUTING $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t mangle -P INPUT $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t mangle -P OUTPUT $policy \
&& $IPTABLES -t mangle -P FORWARD $policy \
|| let ret+=1
;;
*)
let ret+=1
;;
esac
done
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && success || failure
echo
return $ret
}
load_sysctl() {
# load matched sysctl values
if [ -n "$IPTABLES_SYSCTL_LOAD_LIST" ]; then
echo -n $"Loading sysctl settings: "
ret=0
for item in $IPTABLES_SYSCTL_LOAD_LIST; do
fgrep $item /etc/sysctl.conf | sysctl -p - >/dev/null
let ret+=$?;
done
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && success || failure
echo
fi
return $ret
}
start() {
# Do not start if there is no config file.
[ -f "$IPTABLES_DATA" ] || return 1
echo -n $"Applying $IPTABLES firewall rules: "
OPT=
[ "x$IPTABLES_SAVE_COUNTER" = "xyes" ] && OPT="-c"
$IPTABLES-restore $OPT $IPTABLES_DATA
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
success; echo
else
failure; echo; return 1
fi
# Load additional modules (helpers)
if [ -n "$IPTABLES_MODULES" ]; then
echo -n $"Loading additional $IPTABLES modules: "
ret=0
for mod in $IPTABLES_MODULES; do
echo -n "$mod "
modprobe $mod > /dev/null 2>&1
let ret+=$?;
done
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && success || failure
echo
fi
# Load sysctl settings
load_sysctl
touch $VAR_SUBSYS_IPTABLES
return $ret
}
stop() {
# Do not stop if iptables module is not loaded.
[ -e "$PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES" ] || return 1
flush_n_delete
set_policy ACCEPT
if [ "x$IPTABLES_MODULES_UNLOAD" = "xyes" ]; then
echo -n $"Unloading $IPTABLES modules: "
ret=0
rmmod_r ${IPV}_tables
let ret+=$?;
rmmod_r ${IPV}_conntrack
let ret+=$?;
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && success || failure
echo
fi
rm -f $VAR_SUBSYS_IPTABLES
return $ret
}
save() {
# Check if iptable module is loaded
[ ! -e "$PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES" ] && return 1
# Check if firewall is configured (has tables)
tables=`cat $PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES 2>/dev/null`
[ -z "$tables" ] && return 1
echo -n $"Saving firewall rules to $IPTABLES_DATA: "
OPT=
[ "x$IPTABLES_SAVE_COUNTER" = "xyes" ] && OPT="-c"
ret=0
TMP_FILE=`/bin/mktemp -q /tmp/$IPTABLES.XXXXXX` \
&& chmod 600 "$TMP_FILE" \
&& $IPTABLES-save $OPT > $TMP_FILE 2>/dev/null \
&& size=`stat -c '%s' $TMP_FILE` && [ $size -gt 0 ] \
|| ret=1
if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then
if [ -e $IPTABLES_DATA ]; then
cp -f $IPTABLES_DATA $IPTABLES_DATA.save \
&& chmod 600 $IPTABLES_DATA.save \
|| ret=1
fi
if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then
cp -f $TMP_FILE $IPTABLES_DATA \
&& chmod 600 $IPTABLES_DATA \
|| ret=1
fi
fi
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && success || failure
echo
rm -f $TMP_FILE
return $ret
}
status() {
tables=`cat $PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES 2>/dev/null`
# Do not print status if lockfile is missing and iptables modules are not
# loaded.
# Check if iptable module is loaded
if [ ! -f "$VAR_SUBSYS_IPTABLES" -a -z "$tables" ]; then
echo $"Firewall is stopped."
return 1
fi
# Check if firewall is configured (has tables)
if [ ! -e "$PROC_IPTABLES_NAMES" ]; then
echo $"Firewall is not configured. "
return 1
fi
if [ -z "$tables" ]; then
echo $"Firewall is not configured. "
return 1
fi
NUM=
[ "x$IPTABLES_STATUS_NUMERIC" = "xyes" ] && NUM="-n"
VERBOSE=
[ "x$IPTABLES_STATUS_VERBOSE" = "xyes" ] && VERBOSE="--verbose"
COUNT=
[ "x$IPTABLES_STATUS_LINENUMBERS" = "xyes" ] && COUNT="--line-numbers"
for table in $tables; do
echo $"Table: $table"
$IPTABLES -t $table --list $NUM $VERBOSE $COUNT && echo
done
return 0
}
reload() {
IPTABLES_MODULES_UNLOAD="no"
restart
}
restart() {
[ "x$IPTABLES_SAVE_ON_RESTART" = "xyes" ] && save
stop
start
}
case "$1" in
start)
stop
start
RETVAL=$?
;;
stop)
[ "x$IPTABLES_SAVE_ON_STOP" = "xyes" ] && save
stop
RETVAL=$?
;;
reload)
[ -e "$VAR_SUBSYS_IPTABLES" ] && reload
;;
restart)
restart
RETVAL=$?
;;
condrestart)
[ -e "$VAR_SUBSYS_IPTABLES" ] && restart
;;
status)
status
RETVAL=$?
;;
panic)
flush_n_delete
set_policy DROP
RETVAL=$?
;;
save)
save
RETVAL=$?
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|reload|restart|condrestart|status|panic|save}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit $RETVAL
7.安装Layer 7协议
[root@localhost src]# tar xf l7-protocols-2009-05-28.tar.gz -C /usr/src
[root@localhost src]# cd /usr/src/l7-protocols-2009-05-28/
[root@localhost l7-protocols-2009-05-28]# make install
mkdir -p /etc/l7-protocols
cp -R * /etc/l7-protocols
[root@localhost l7-protocols-2009-05-28]#
8.测试
[root@localhost l7-protocols-2009-05-28]# iptables -m layer7 –help #查看帮助信息
iptables v1.4.7
Usage: iptables -[AD] chain rule-specification [options]
iptables -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification [options]
iptables -R chain rulenum rule-specification [options]
iptables -D chain rulenum [options]
iptables -[LS] [chain [rulenum]] [options]
iptables -[FZ] [chain] [options]
iptables -[NX] chain
iptables -E old-chain-name new-chain-name
iptables -P chain target [options]
iptables -h (print this help information)
Commands:
Either long or short options are allowed.
--append -A chain Append to chain
--delete -D chain Delete matching rule from chain
--delete -D chain rulenum
Delete rule rulenum (1 = first) from chain
--insert -I chain [rulenum]
Insert in chain as rulenum (default 1=first)
--replace -R chain rulenum
Replace rule rulenum (1 = first) in chain
--list -L [chain [rulenum]]
List the rules in a chain or all chains
--list-rules -S [chain [rulenum]]
Print the rules in a chain or all chains
--flush -F [chain] Delete all rules in chain or all chains
--zero -Z [chain [rulenum]]
Zero counters in chain or all chains
--new -N chain Create a new user-defined chain
--delete-chain
-X [chain] Delete a user-defined chain
--policy -P chain target
Change policy on chain to target
--rename-chain
-E old-chain new-chain
Change chain name, (moving any references)
Options:
[!] --proto -p proto protocol: by number or name, eg. `tcp'
[!] --source -s address[/mask][...]
source specification
[!] --destination -d address[/mask][...]
destination specification
[!] --in-interface -i input name[+]
network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
--jump -j target
target for rule (may load target extension)
--goto -g chain
jump to chain with no return
--match -m match
extended match (may load extension)
--numeric -n numeric output of addresses and ports
[!] --out-interface -o output name[+]
network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
--table -t table table to manipulate (default: `filter')
--verbose -v verbose mode
--line-numbers print line numbers when listing
--exact -x expand numbers (display exact values)
[!] --fragment -f match second or further fragments only
--modprobe=<command> try to insert modules using this command
--set-counters PKTS BYTES set the counter during insert/append
[!] --version -V print package version.
layer7 match options:
--l7dir <directory> : Look for patterns here instead of /etc/l7-protocols/
(--l7dir must be specified before --l7proto if used)
[!] --l7proto <name>: Match named protocol using /etc/l7-protocols/.../name.pat
[root@localhost l7-protocols-2009-05-28]#
9.重新启动iptables
[root@localhost ~]# service iptables restart
10.封qq,酷狗,迅雷等
封QQ
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.10.0/24 -m layer7 --l7proto qq -j DROP
封酷狗
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.10.0/24 -m layer7 --l7proto kugoo -j DROP
封迅雷
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.10.0/24 -m layer7 --l7proto xunlei -j DROP
11.查看支持的协议
[root@localhost ~]# ls /etc/l7-protocols/protocols/
100bao.pat doom3.pat jabber.pat radmin.pat teamfortress2.pat
aim.pat edonkey.pat kugoo.pat rdp.pat teamspeak.pat
aimwebcontent.pat fasttrack.pat live365.pat replaytv-ivs.pat telnet.pat
applejuice.pat finger.pat liveforspeed.pat rlogin.pat tesla.pat
ares.pat freenet.pat lpd.pat rtp.pat tftp.pat
armagetron.pat ftp.pat mohaa.pat rtsp.pat thecircle.pat
battlefield1942.pat gkrellm.pat msn-filetransfer.pat runesofmagic.pat tonghuashun.pat
battlefield2142.pat gnucleuslan.pat msnmessenger.pat shoutcast.pat tor.pat
battlefield2.pat gnutella.pat mute.pat sip.pat tsp.pat
bgp.pat goboogy.pat napster.pat skypeout.pat unknown.pat
biff.pat gopher.pat nbns.pat skypetoskype.pat unset.pat
bittorrent.pat guildwars.pat ncp.pat smb.pat uucp.pat
chikka.pat h323.pat netbios.pat smtp.pat validcertssl.pat
cimd.pat halflife2-deathmatch.pat nntp.pat snmp.pat ventrilo.pat
ciscovpn.pat hddtemp.pat ntp.pat socks.pat vnc.pat
citrix.pat hotline.pat openft.pat soribada.pat whois.pat
counterstrike-source.pat http.pat pcanywhere.pat soulseek.pat worldofwarcraft.pat
cvs.pat http-rtsp.pat poco.pat ssdp.pat x11.pat
dayofdefeat-source.pat ident.pat pop3.pat ssh.pat xboxlive.pat
dazhihui.pat imap.pat pplive.pat ssl.pat xunlei.pat
dhcp.pat imesh.pat qq.pat stun.pat yahoo.pat
directconnect.pat ipp.pat quake1.pat subspace.pat zmaap.pat
dns.pat irc.pat quake-halflife.pat subversion.pat
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]#ls /etc/l7-protocols/protocols/ | wc -l
114
大家可以看到,可以支持114个协议,嘿嘿!至此所有演示全部结束,^_^ ……