go http roundtrip
Golang http.RoundTripper 笔记
[](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016153599)
RoundTripper is an interface representing the ability to execute a single HTTP transaction, obtaining the Response for a given Request.
对于http客户端,可以使用不同的实现了 RoundTripper 接口的Transport实现来配置它的行为
RoundTripper 有点像 http.Client 的中间件
接口定义
type RoundTripper interface {
RoundTrip(*Request) (*Response, error)
}
需要实现RoundTrip函数
type SomeClient struct {}
func (s *SomeClient) RoundTrip(r *http.Request)(*Response, error) {
//Something comes here...Maybe
}
场景
原文: https://lanre.wtf/blog/2017/0...
缓存 responses,比如 app需要访问 Github api,获取 trending repos,这个数据变动不频繁,假设30分钟变动一次,你显然不希望每次都要点击api都要来请求Github api,解决这个问题的方法是实现这样的
http.RoundTripper- 有缓存时从缓存取出response数据
- 过期,数据通过重新请求api获取
- 有缓存时从缓存取出response数据
根据需要设置http header, 一个容易想到的例子go-github一个Github的 api的go客户端。某些github api不需要认证,有些需要认证则需要提供自己的http client,比如 ghinstallation,下面是ghinstallation 的 RoundTrip 函数实现,设置 Authorization 头
- 限速(Rate limiting) 控制请求速率
实际的例子
实现http.RoundTripper 缓存 http response的逻辑。
一个http server的实现
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// server/main.go
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
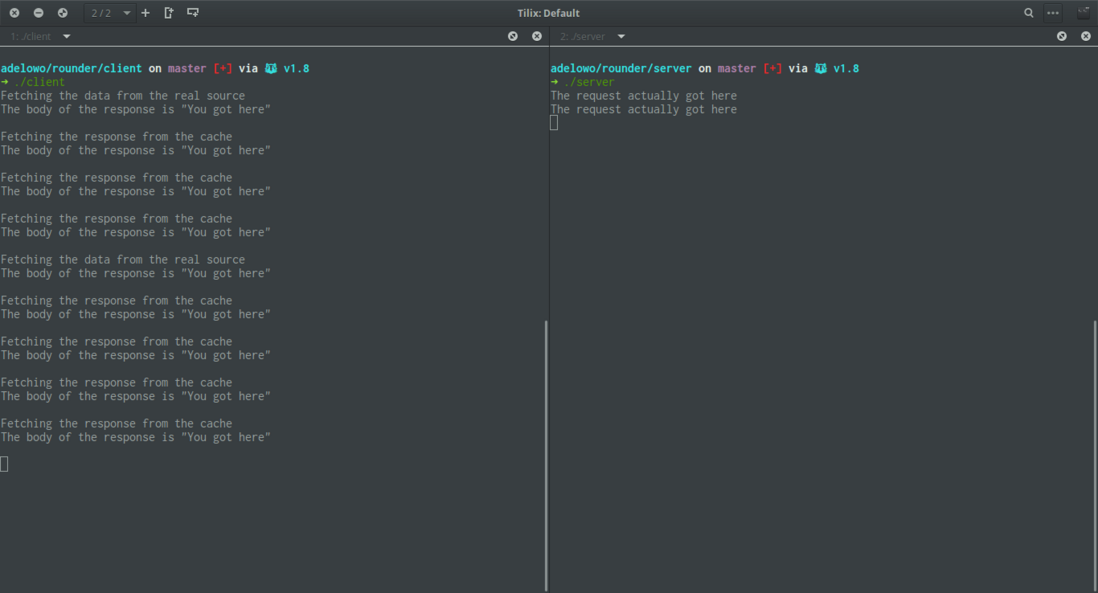
// This is here so we can actually see that the responses that have been cached don't get here
fmt.Println("The request actually got here")
w.Write([]byte("You got here"))
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8000", mux)
}
http client中创建新的 http.Transport 实现 http.RoundTripper接口
主程序main实现
https://github.com/adelowo/ro...
func main() {
cachedTransport := newTransport()
// cachedTransport 是自定义实现http.RoundTripper接口的 Transport
client := &http.Client{
Transport: cachedTransport,
Timeout: time.Second * 5,
}
// 每5秒清除缓存
cacheClearTicker := time.NewTicker(time.Second * 5)
//每秒请求一次,可以看出response是从缓存获取还是从服务器请求
reqTicker := time.NewTicker(time.Second * 1)
terminateChannel := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(terminateChannel, syscall.SIGTERM, syscall.SIGHUP)
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "http://localhost:8000", strings.NewReader(""))
if err != nil {
panic("Whoops")
}
for {
select {
case <-cacheClearTicker.C:
// Clear the cache so we can hit the original server
cachedTransport.Clear()
case <-terminateChannel:
cacheClearTicker.Stop()
reqTicker.Stop()
return
case <-reqTicker.C:
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("An error occurred.... %v", err)
continue
}
buf, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("An error occurred.... %v", err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("The body of the response is \"%s\" \n\n", string(buf))
}
}
}
cacheTransport 中 RoundTrip 函数实现读取缓存中的reponse
func (c *cacheTransport) RoundTrip(r *http.Request) (*http.Response, error) {
// Check if we have the response cached..
// If yes, we don't have to hit the server
// We just return it as is from the cache store.
if val, err := c.Get(r); err == nil {
fmt.Println("Fetching the response from the cache")
return cachedResponse([]byte(val), r)
}
// Ok, we don't have the response cached, the store was probably cleared.
// Make the request to the server.
resp, err := c.originalTransport.RoundTrip(r)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Get the body of the response so we can save it in the cache for the next request.
buf, err := httputil.DumpResponse(resp, true)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Saving it to the cache store
c.Set(r, string(buf))
fmt.Println("Fetching the data from the real source")
return resp, nil
}
运行结果
links: